BIO-materials R&D
Exosome Tech.
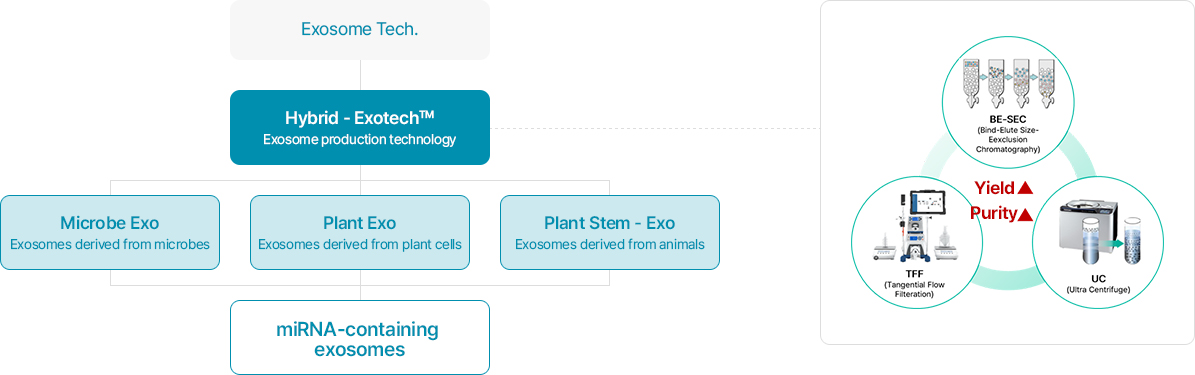
Hybrid-Exotech™
This is a process for isolating exosomes using materials secured based on GFC Life Science's skin microbiome and Higher Plant Cell technology. Exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that originate from endosomes inside cells and are released to the outside. They are nano particles with a diameter of less than 200nm and act as messengers between cells. GFC Life Science applies Hybrid-Exotech™, its proprietary exosome extraction process, to isolate ultra-pure, high-yield exosomes from not only human stem cell culture media but also various lactic acid bacteria cell lines and more than 50 types of plant callus cultures that it owns.
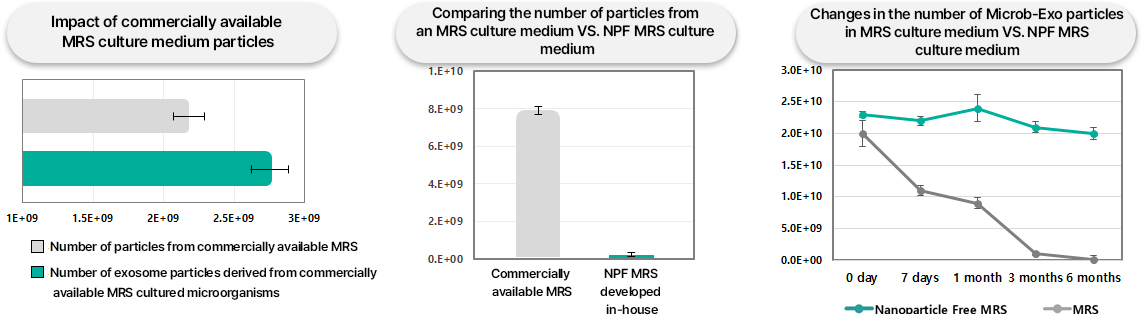
Our company is developing “Microbe-Exo,” a microbial-derived exosome, using the skin microbiome acquired through our Genovation platform. To develop high-purity Microbe-Exo, we developed a Nano Particle Free (NPF) culture medium with exosome-like particles removed using our own technology to secure high-purity exosomes. We also confirmed that the particle number of these was more stable for a long period of time than exosomes obtained through general commercially available media.
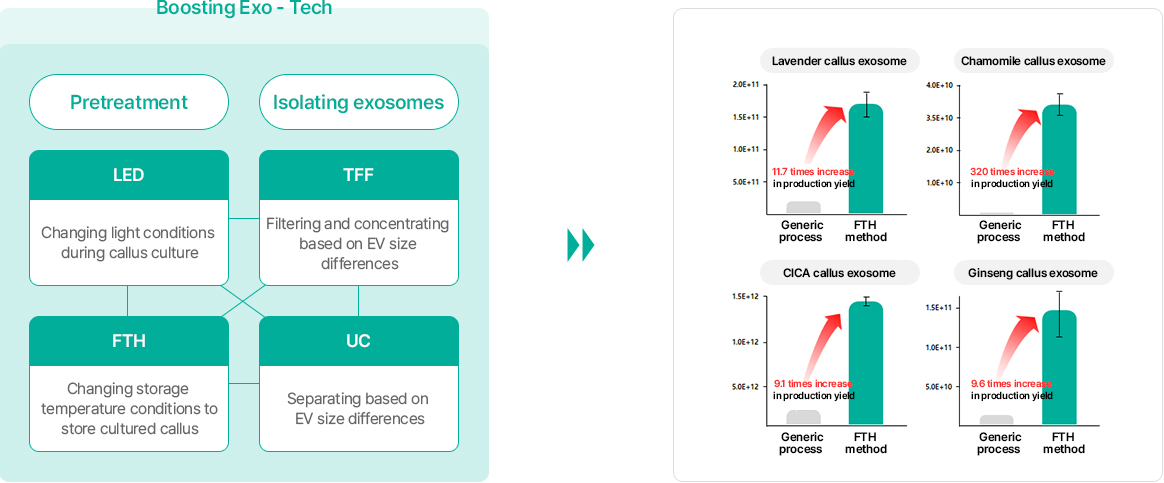
Our company is developing what it calls the “Plant Stem-Exo,” a plant-derived exosome, using plant cells obtained using the Plant EVeration Cell Tech. Since plant cells have cell walls and all have different physiological characteristics, it is difficult to industrialize plant-derived exosomes by establishing a process that uses a standardized method. As such, GFC Life Science is producing ultra-pure, high-yield “Plant Stem-Exo” by applying a process suited to the characteristics of each Higher Plant Cell using Boosting Exo-Tech, which is our proprietary technology.
Exosomes are nano-sized particles, and most researchers rely on Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) to validate them. However, this validation method has limitations in accurately verifying exosomes because it can only measure liposomes or similar nanoparticles, and not exosomes specifically. GFC Life Science has secured the miRNAs of each exosome that can be used as biomarkers through analysis of small RNAs within the exosomes of each plant material, and is conducting quantitative QC analysis of these. Our company validates exosomes using exosome-specific proteins as well.
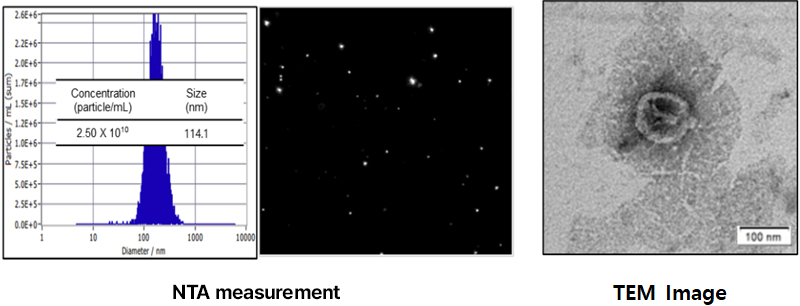
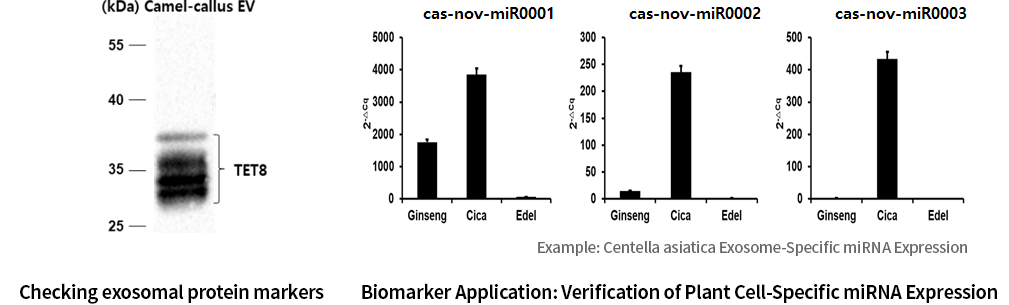
In order to validate exosomes derived from plant cells, GFC Life Science is analyzing proteins with Tetraspanin 8 (TET8), an exosome-specific membrane protein, in addition to existing NTA and TEM analyses. Meanwhile, we focused on miRNAs in exosomes and conducted miRNA analysis using small RNA sequencing of exosomes and callus cultures from more than 20 plant species. As a result, we have successfully secured a large number of exosomal miRNAs, developed a validation method to utilize them as biomarkers, and are currently standardizing the process.
Our company is also developing “membrane-fused hybrid exosome” technology and “active-loaded hybrid exosome” technology to keep pushing exosomes as a functional material and secure future growth technologies.
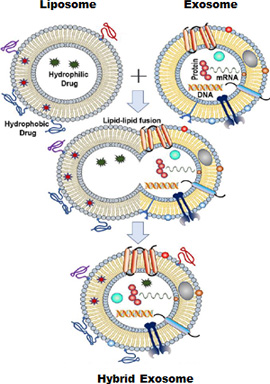
Membrane-fused hybrid exosomes
Our company is developing hybrid exosomes by fusing the membrane of exosomes and liposomes, which can be used as highly functional cosmetic material capable of directly delivering desired effects to specific locations by addressing some of the shortcomings liposomes have.
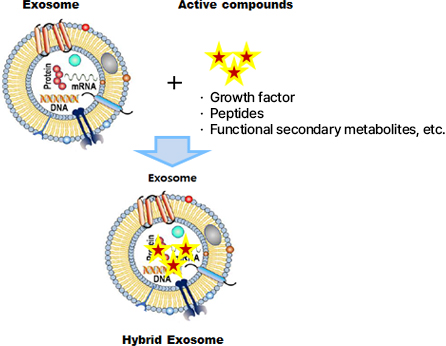
Active-loaded hybrid exosomes
Our company is designing experiments to prove the production of active-loaded hybrid exosomes and develop scientifically proven, highly functional materials by measuring capture efficiency and experiments comparing efficacies.
