NGS data on skin flora analysis and change analysis of 500 Korean test subjects were secured and database was built to be used as a core resource for skin microbiome research.
BIO-materials R&D
Skin Microbiome
Skin Microbiome
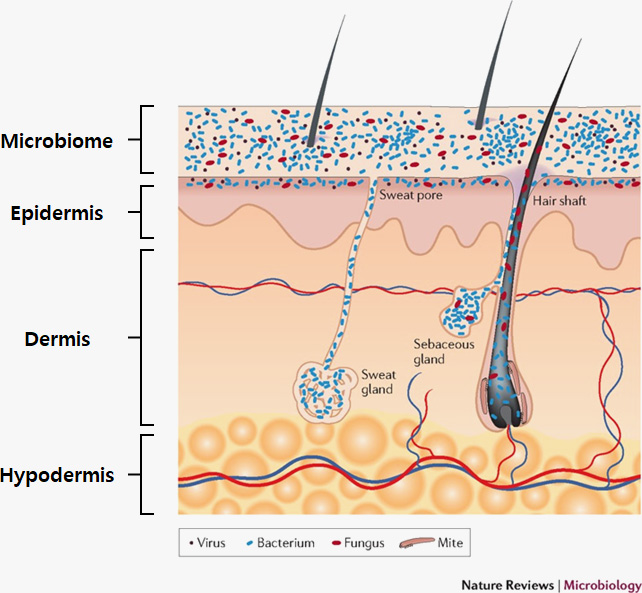
The skin microbiome is a general term for microorganisms living on the skin. The skin microbiome is the latest addition to what we know makes up our skin - previously the skin was believed to have the epidermis, dermis, and fatty layer, but now we know it has a fourth microbiome layer.
Skin Microbiome
According to a 2018 Nature Review Microbiology study, the effective interaction of skin flora has a high correlation with the diversity of the skin microbiome and skin health. Such a symbiotic relationship between the skin and the skin microbiome is called “Crosstalk” and is recognized as an important factor in skin immunity and health. GFC Life Science has successfully isolated and possesses various strains including human-derived lactic acid bacteria, and has secured technology through research on the microbiome and related effects. By conducting multifaceted research on this, our company has acquired the original technology to materialize microorganisms capable of controlling the skin microbiome. We also utilize the skin microbiome as genetic resources and to verify the effectiveness of products. In particular, our company is developing high value-added functional products using microorganisms through differentiated research and market approaches, especially skin microbiome technology, which goes far beyond simply using and consuming skin microorganisms.
Genovation platform
Genovation platform is a platform for developing GFC Life Science's own microbiome cosmetic materials using the Genovation DB, Genovation Bank, and technology from Genovation Tech.
Genovation DB
Genovation DB is discovering and compiling meaningful correlations between skin clinical data and the skin microbiome.
Genovation Bank
Our company has built a library of approximately 2,000 skin microbiome strains via Genovation Banking.
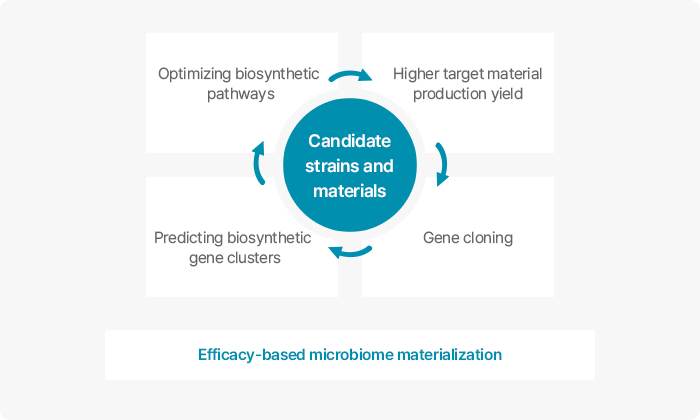
Genovation Tech.
Genovation Tech. maximizes the efficacy and production yield of acquired strains to help use as materials for cosmetic applications.
Genovation DB
GFC Life Science is securing and compiling metagenome data on the dominance and cluster changes of major skin flora from Korean test subjects, and utilizing it for skin microbiome research. Moreover, our company conducts metabolomics research by analyzing the differences in metabolites between the culture medium and the cells according to the medium during strain cultivation. We secure data on which metabolites affect the changes in the community of skin flora and compile it into a database.

Genovation DB Process
GFC Life Science is also building a database by analyzing genomes and metabolites using NGS technology and LC/Q-TOF and studying the correlation between the two.
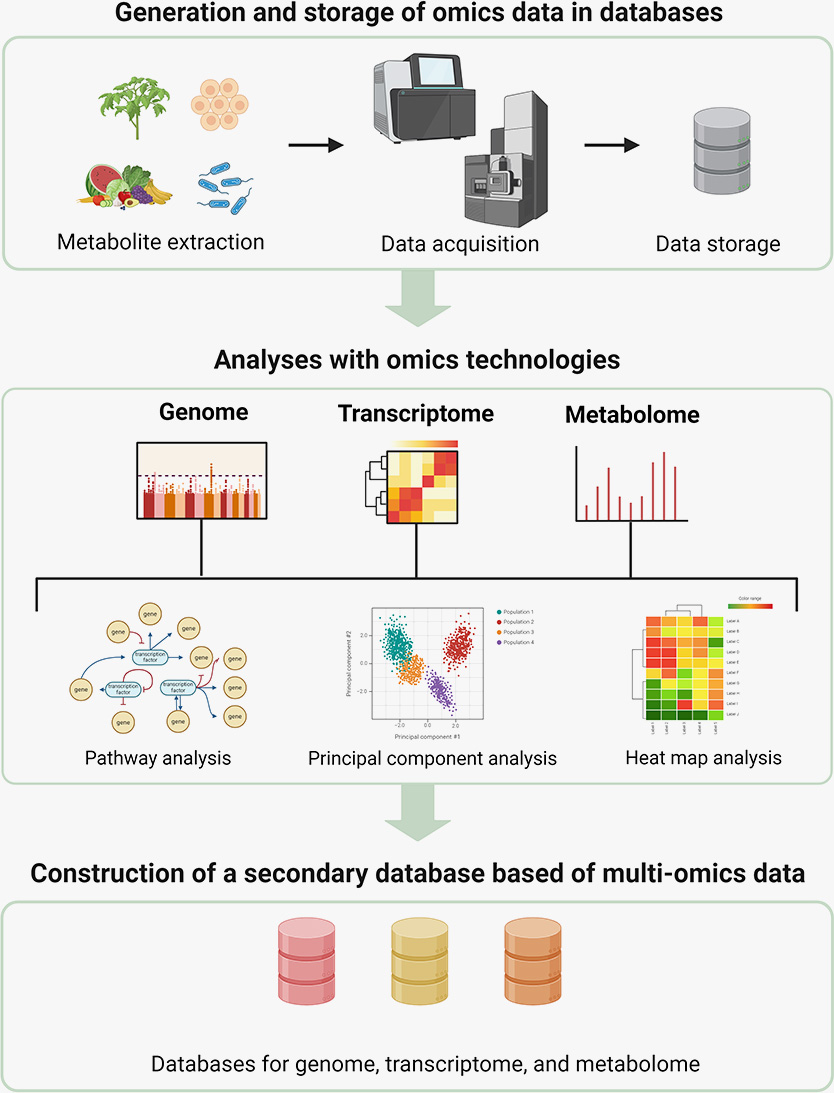
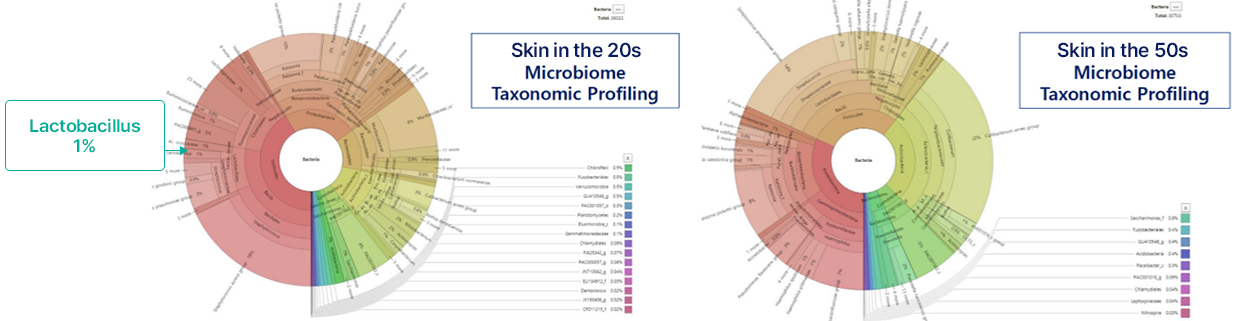
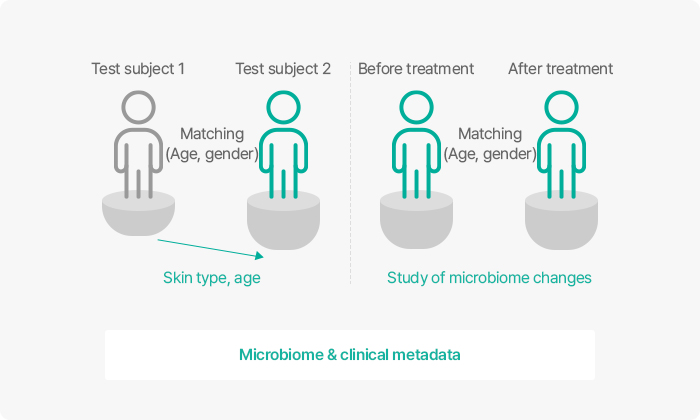
GFC Life Science is conducting research to build a skin microbiome database based on various factors such as skin type, age, and disease.
Research results showed that Lactobacillus content was higher in the skin of younger test subjects (20s), and based on this, GFC Life Science is in the process of establishing a platform to identify the Lactobacillus found in the younger age group and utilize them as a pipeline.
NGS data on skin flora analysis and change analysis of 500 Korean test subjects were secured and database was built to be used as a core resource for skin microbiome research
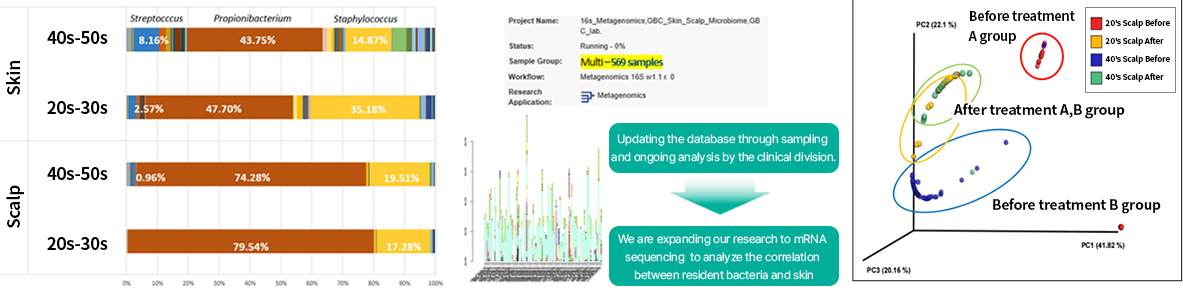
Confirmed the potential as a skin health improvement factor through a skin flora regulation function test
With research, we have confirmed that the microbiome group structure that exists depending on the age of a subject and skin area tends to be distinct. Thus, we are currently analyzing this in combination with factors such as lifestyle habits and history of skin disease to compile a database. Additionally, GFC Life Science is utilizing the data to derive meaningful microbiome group changes after processing samples for various products being developed.
Compiled analysis data for metabolite analysis, identified a proprietary strain (L. paracasei GFC07), and compiled a database
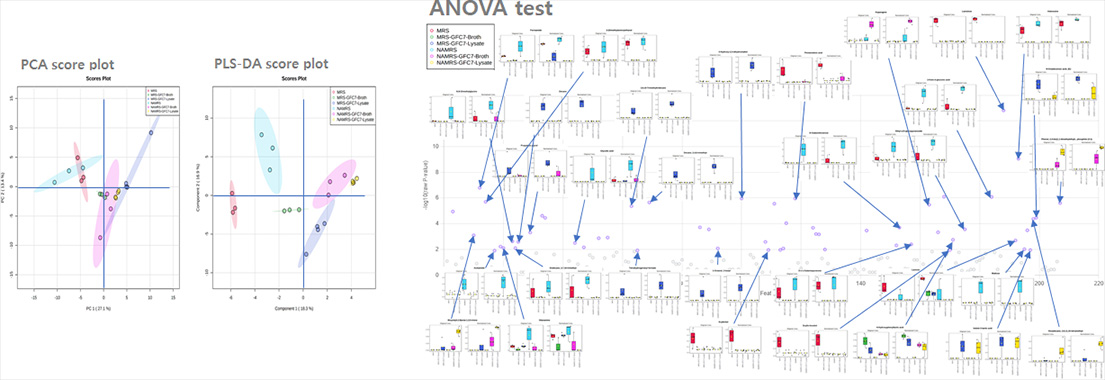
Confirmed the potential as a skin health improvement factor through a skin flora regulation function test
GFC Life Science is using metabolome analysis to reveal which metabolites are indeed effective.
Genovation Banking
This is GFC Life Science's library and preservation system for natural products and skin-derived strains, which are considered unique and high value-adding biological resources for our company..
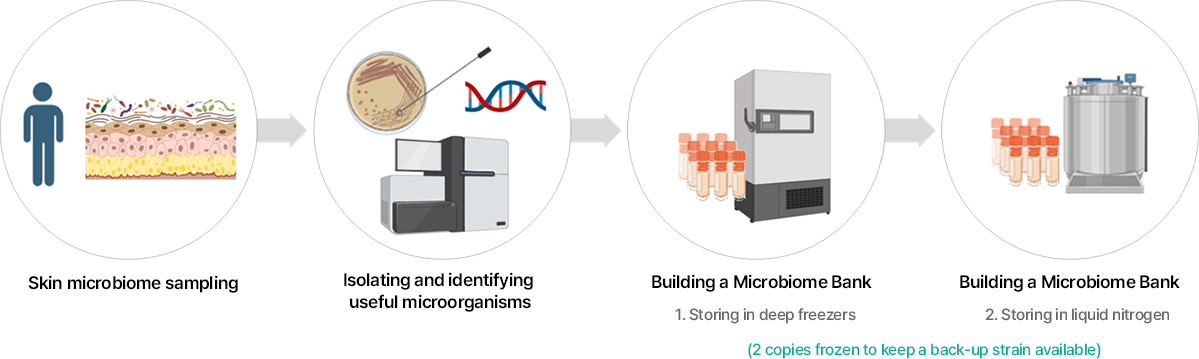
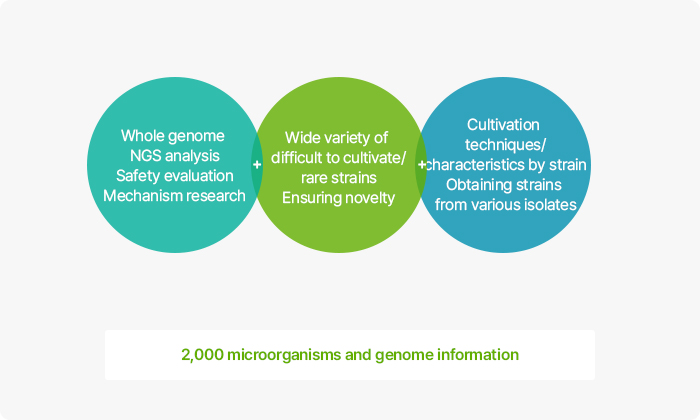
Acquired strains with skin-related efficacies and compiled a library of such strains (currently, approximately 2,000 strains stored / research to apply as cosmetic materials)
Our company has isolated more than 2,000 strains, analyzed the strains' species names through phylogenetic research, built a microbiome bank with two copies, and stored them for use in the development and research of skin microbiome materials. We are also expanding our pipeline with materials for various purposes such as improving wrinkles and brightening the skin.
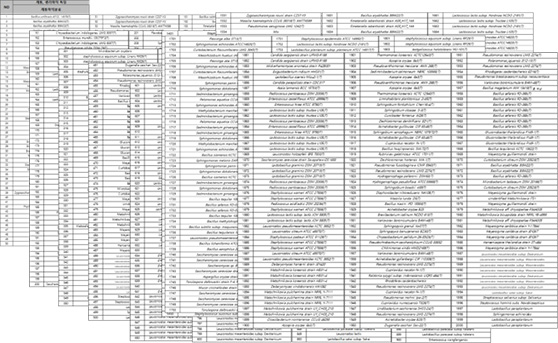
Skin microbiome strain library
Since the skin microbiome varies depending on race, environment, and genetic factors, securing a variety of useful strains must take priority before selecting a material that suits the desired purpose..
Rather than simply getting our hands on a large number of strains, GFC Life Science can identify strains with statistically significant differences through Genovation DB technology, and has secured approximately 2,000 strains to date using Genovation Banking technology.

Phylogenetic tree of strains beneficial to the skin
At present, GFC Life Science's library has isolated useful microorganisms that live not only in the skin microbiome but also in natural products such as plants and fruits, fermented foods, and natural environmental conditions such as soil and aquatic systems. Our company ensures the safety, reliability, and efficacies of these acquired strains through in vitro and in vivo studies, and it continues to research new ways to apply them as cosmetic materials.
Using Genovation Banking technology, we have secured skin microbiomes and beneficial microorganisms living in the natural environment, and have contributed to securing intellectual property rights by depositing patents, general deposits, and academic publications for the strains we have isolated and identified in-house.
Our patented strains are then developed into a wide range of products with further in-depth research and development, and we also conduct customized research and product development for customers by utilizing the library.
Most of the top probiotics products currently distributed in the domestic market use imported strains, thus they incur royalty payments to their original sources. Also, with the Nagoya Protocol taking effect, additional profit distribution is essential, as such securing useful microbial materials in the strain market is considered a way to boost a company’s competitiveness as well.
More 2,000 strains secured by GFC Life Science will be a great source competitiveness in using them as cosmetic materials.
Genovation Tech. - Bioinformatics
Genovation Tech.'s bioinformatics technology predicts the utility of candidate strains based on genomic analysis. Analyzing the genome of different strains can prove novelty by selecting unique genes, and can be applied to biotechnology by analyzing the metabolic potential of candidate strains.
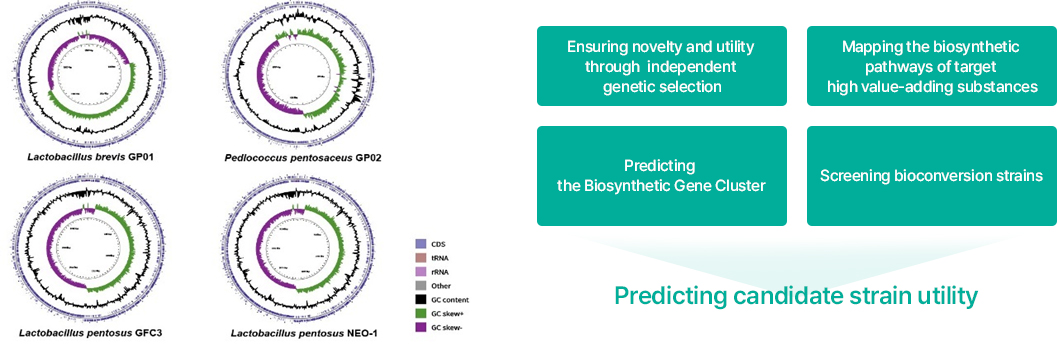
Genovation Tech. - Biotechnology
Genovation Tech.'s Biotechnology maximizes the utility of selected strains and materials and increases production yields. Strains selected using bioinformatics technology can be deployed to selectively synthesize substances with a bioconversion process, and genetic recombination can help secure productivity and economic feasibility.
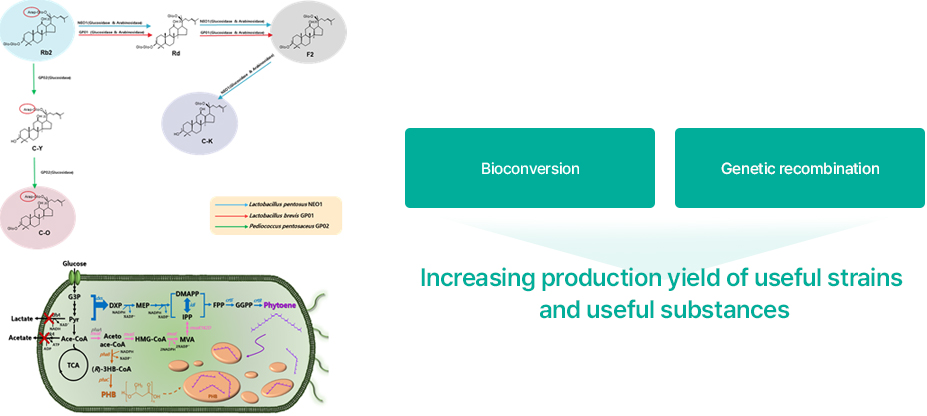
Applying technology from Genovation Tech.
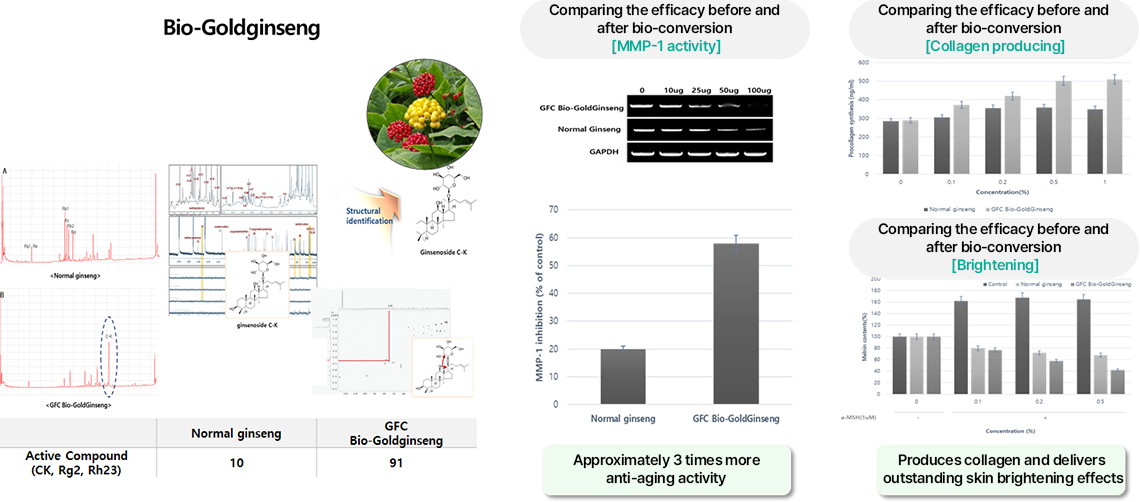
An example of a material developed using GFC Life Science’s Genovation Tech. technology is Bio-Goldginseng. Bio-Goldginseng is a substance that maximizes production yield and efficacy by increasing the minor saponin content found in ginseng. Using Genovation Tech. technology, we first screened for strains that have the ginseng minor saponin synthesis enzyme, and then adjusted them so that they could selectively synthesize the desired substance.